Gender Pay Gap Report 2025
What is the Gender Pay Gap?
The gender pay gap is the difference in the average hourly pay of men and women across an organisation, expressed as a percentage of average male earnings. It compares the pay of all men and all women, not just those performing the same roles, working similar hours, or possessing identical qualifications, competencies or experience.
Why Are We Reporting?
Under the Gender Pay Gap Information Act 2021, all organisations with over 50 employees must report on their hourly gender pay gap across a range of metrics.
What is Our Snapshot Date?
Our snapshot date was 29th June 2025, covering pay data from 1st July 2024 to 29th June 2025
Hourly Pay & Bonus Gaps
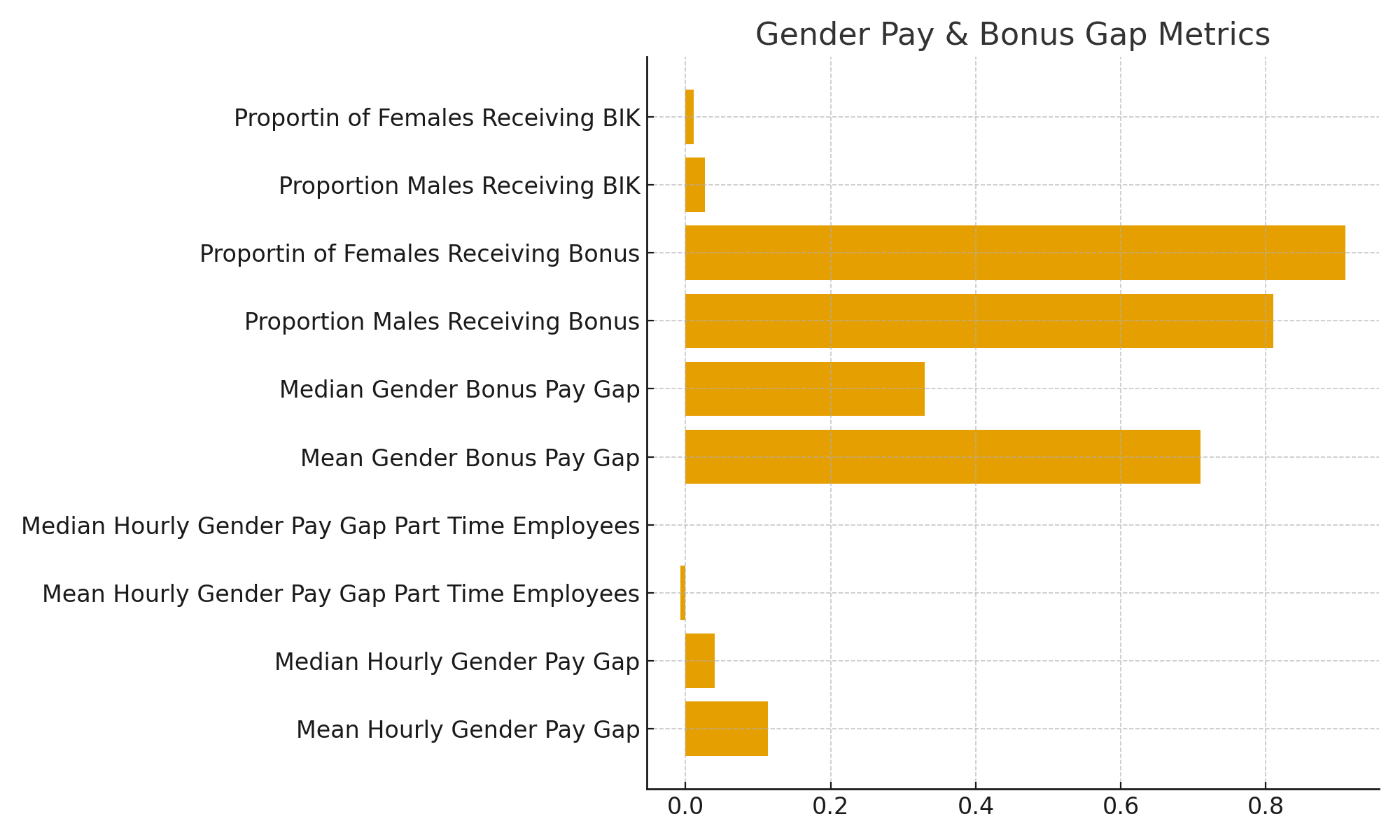
Hourly Pay- Mean Gender Pay Gap: 11.37% - Median Hourly Pay Gap: 4% - Mean Hourly Pay Gap (part-time): -0.73% - Median Hourly Pay Gap (part-time): 0%
|
Bonus Pay- Mean Bonus Pay Gap: 71% - Median Bonus Pay Gap: 33% - % of males receiving bonus pay: 81% - % of females receiving bonus pay: 91% - % of males receiving BIK: 2.7% - % of females receiving BIK: 1.16% We have no temporary employees. |
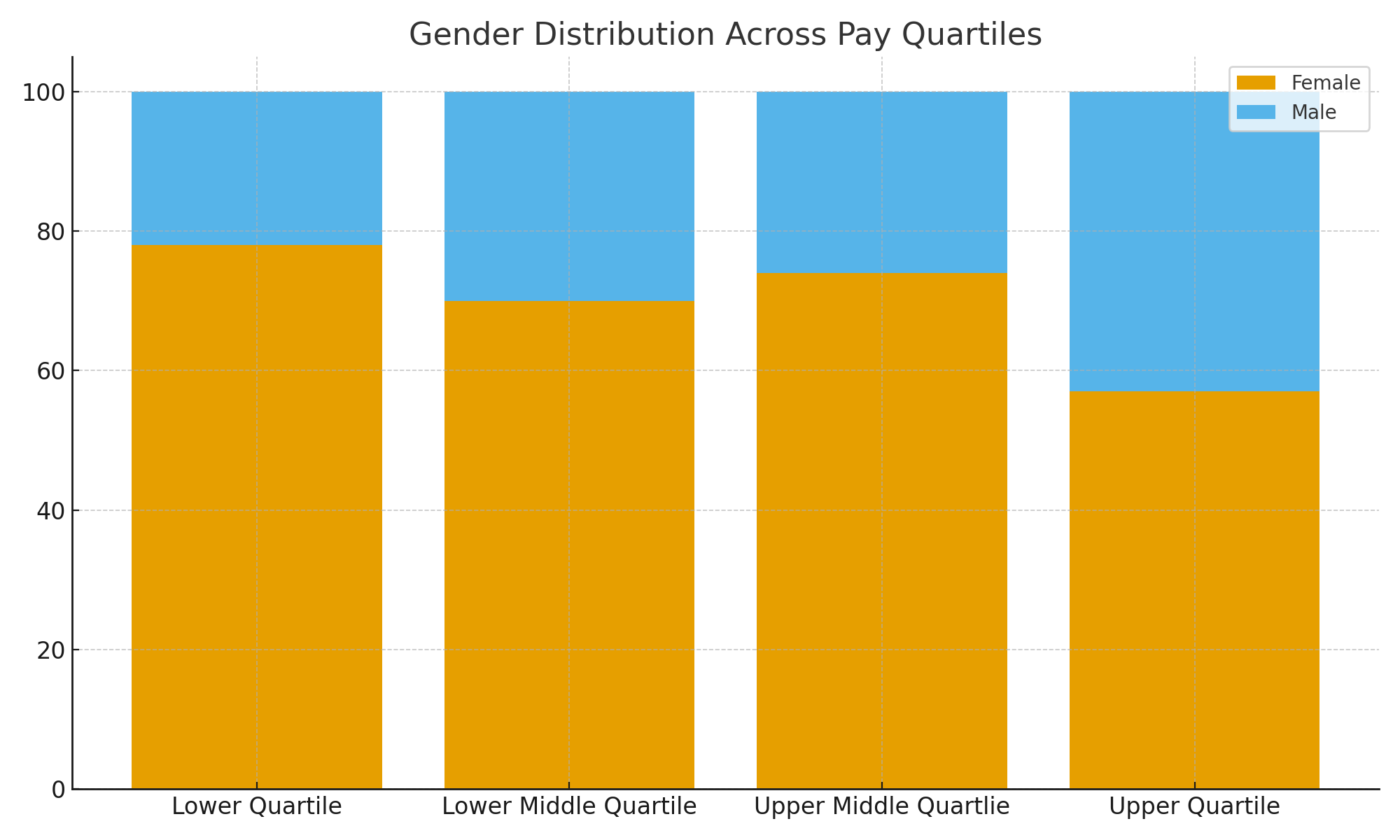
Gender Distribution Across Pay Quartiles
Pay Quartiles
Lower Quartile:- Male: 22% - Female: 78% |
Lower Middle Quartile:- Male: 30% - Female: 70% |
Upper Middle Quartile:- Male: 26% - Female: 74% |
Upper Quartile:- Male: 43% - Female: 57% |
Findings & Action Plan
Gender Pay Gap
Our mean gender pay gap is 11.37%. National research in 2024 reported a mean national gender pay gap of 11.1%. Our own gap is influenced by organisational structure, with females representing a large share of the workforce, especially in lower and lower-middle quartiles. Meanwhile, operational management roles tend to have a higher proportion of male employees.
Mean Bonus Pay Gap
Our mean bonus pay gap is 71%. This is mainly driven by a small number of higher-value bonuses linked to certain management roles. With more males in these positions, this increases the average bonus awarded to male employees. The median bonus gap of 33% arises due to the smaller per centage of men employed overall (30%) with 46% of males employed full time compared to 19% of females in full time positions. Bonus’s paid to full time staff would be greater than part time hence the median gap.
Action Plan
- Ensure gender equality in recruitment, development, and progression.
- Provide training on Diversity, Inclusion, and Unconscious Bias for recruitment personnel.
- Communicate our Equal Opportunities Policy widely to ensure equal access for all.
- Continue supporting internal training and development pathways that encourage female progression into supervisory and management roles.